Computing Stack
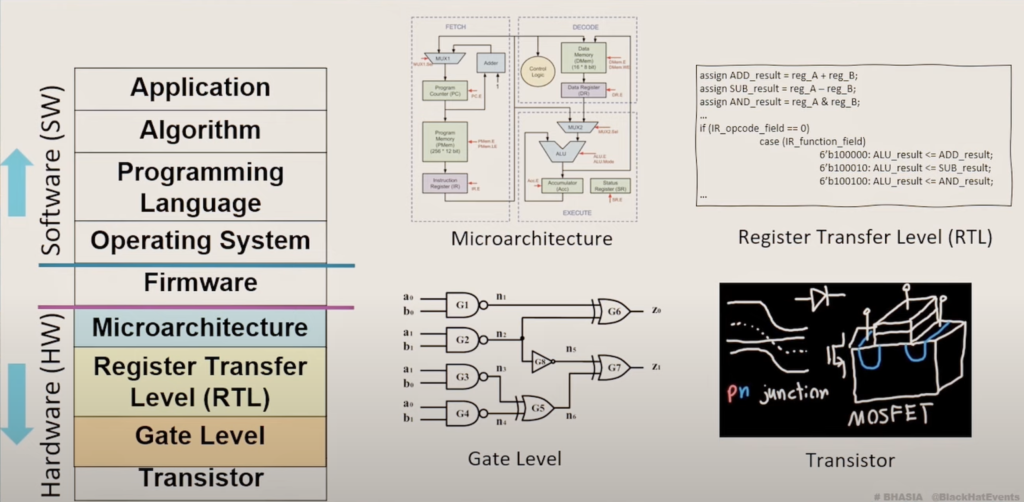
Challenges
Observed During Offensive Security Research at Intel
- Awareness of Hardware Common Weaknesses [CONCEPTS]
- Security-Aware Design Automation [TOOLS]
- “Shift-Left” to Detect & Fix Bugs in RTL [BEST PRACTICES]
1. Limited Awareness of HW Security Weaknesses
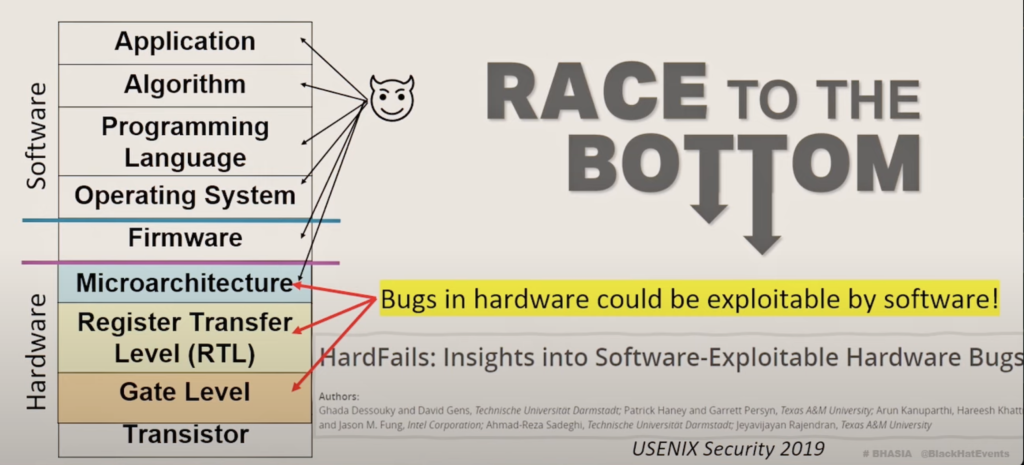
2. Need for Security-Aware Design Automation Tools
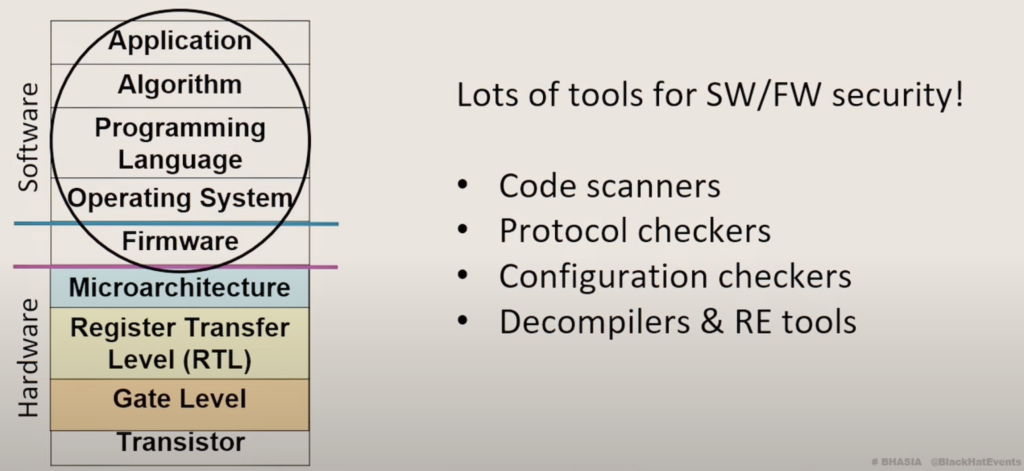

3. Need to Detect/Fix Bugs at RTL Design Phase
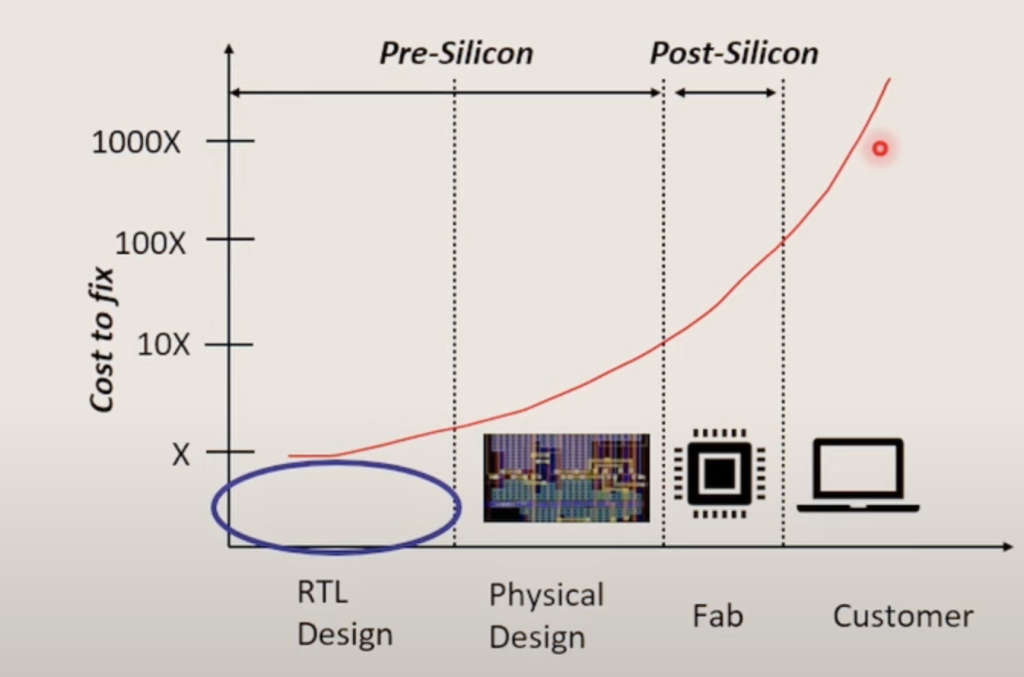
- SW bugs fixed with patches
- HW bugs are complicated to fix
- Time consuming
- Expensive
- Cause brand damage
System on a Chip(Soc)

- Data Confidentiality
- Protect secrets from unauthorized access
- Data Integrity
- Protect data modification by untrusted agents
- Availablity
- Protect against permanent damage to system
- Security features examples
- Execution core & debug privilege checks
- Access control
- Memory encryption & integrity
- Secure data erase
- Power and thermal critical trip alerts
Hack@DAC
- A buggy SoC* framework for furthering innovation
- Realistic security features, thread model, and security objectives
- Vulnerabilities inspired by CVEs and real-world bugs
- Open source and commercial tool support
- Benchmark for developing and testing HW security tools
- Closest to commercial chip designs
- Participants gain hardware security assurance experience
- Develop hacker mindset
- Launchpad for researchers from adjacent areas (e.g., Firmware)

MITRE Hardware CWE


Security-Aware Tooling & Bug Detection

Hack@DAC SoC framework
- Realistic threat model and security objectives
- Closest available to commercial chip designs
- Uncover new classes of security vulnerabilities
- New tools for identifying weakness classes
Black Hat Sound Bytes
- Increased HW Security Awareness
- MITRE HW CWE
- Corpus of weaknesses and code examples
- Open-sourced buggy SoC design
- Realistic security features
- CVE-inspired vulnerabilities
- Complexity matching commercial chips
- Innovations in HW security tooling
- Tools that detect and patch bugs at RTL
- Participants developed hacker mindset